Root Hair Cell Diagram Simple

Here the root surface is covered by fine unicellular root hairs which do the actual absorption of solutes.
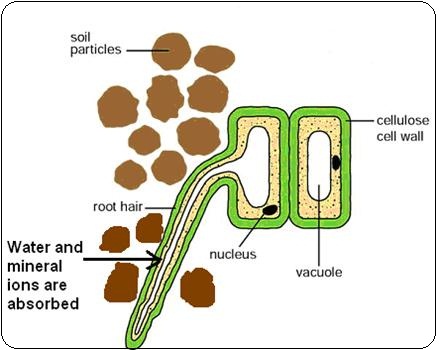
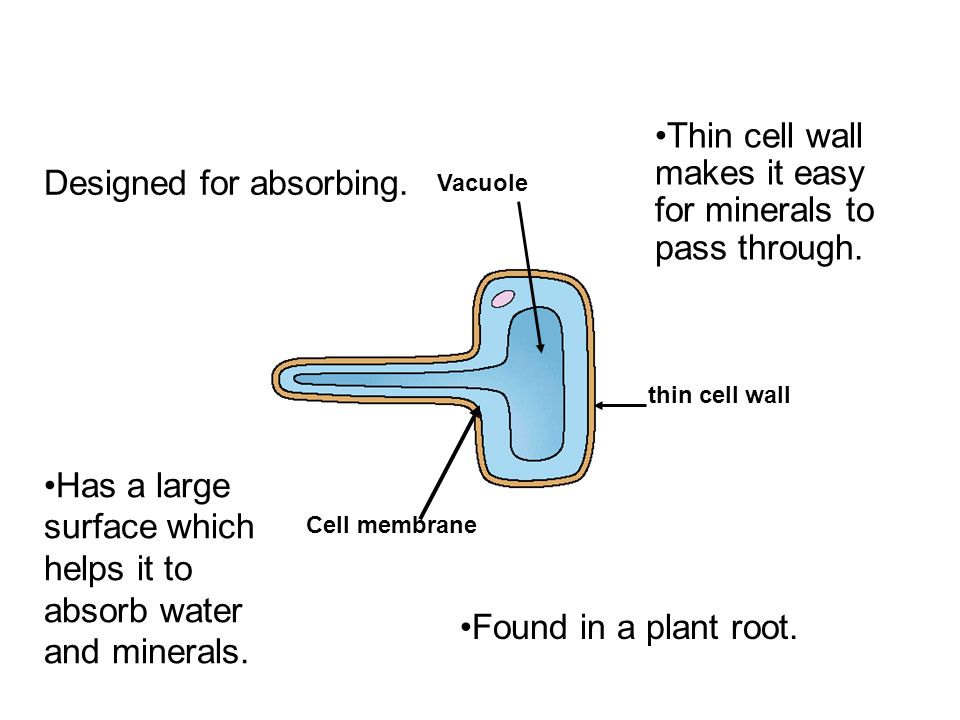
Root hair cell diagram simple. Friction with soil is continually wearing out and destroying the root hairs while the region of growth as it extends downwards by growth is developing new root hairs forming new root hair regions. They are lateral extensions of a single cell and invisible to the naked eye and light microscope. They are found only in the region of maturation of the root. The structure of a root hair cell differs from other root cells in that it has a long thin extension supported by the central vacuole which greatly increases its surface area.
The function of root hairs is to collect water and mineral nutrients from the soil. They are long and thin so they can penetrate between soil particles and they have a large surface area for absorption of water. This clip is from. Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis.
A look at the structure and function of the root hair cell an example of a specialised plant cell. This allows the root hair coverage to remain the same despite root hairs constantly dying. These cells constantly form at the top of the root of the plant so as others die new ones take their place. This is a labelled diagram of a root hair cell.
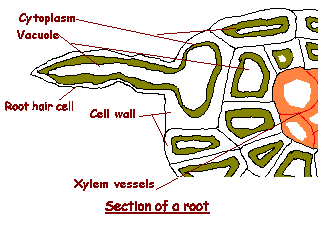
Energy from the sun is eventually used to convert water into hydrogen and oxygen. This solution goes up through the roots to the rest of the plant. The water absorbed by the root hair cells passes through the plant in xylem tubes and eventually reaches the leaves. A root hair or absorbent hair the rhizoid of a vascular plant is a tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast a hair forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root as they are lateral extensions of a single cell and only rarely branched they are visible to the naked eye and light microscope.
The root hairs are where most water absorption happens. Like other root cells it has a thick cell wall huge central vacuole and is separated from other root cells by a thin layer of cytoplasm. Hydrogen is combined with the carbon dioxide to produce the food glucose for the. Key stage three bitesize revision.
A root hair of a vascular plant is a tubular outgrowth of a hair forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root. The function of the root hair cell is to obtain water from the ground and transport this to the xylem.