Root Hair Cell Drawing Easy

A look at the structure and function of the root hair cell an example of a.
Root hair cell drawing easy. After cells start to elongate and mature no further extension takes place and the root is stationary for the rest of its life. Pupils could investigate the concept by drawing the cross section of the root and then drawing another without. As the cells of root hair zone become mature the root hairs shrivel and become non functional. Just behind the root cap is 2 the very short growing region.
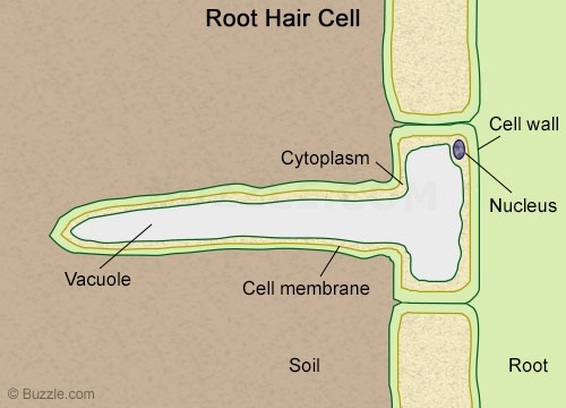
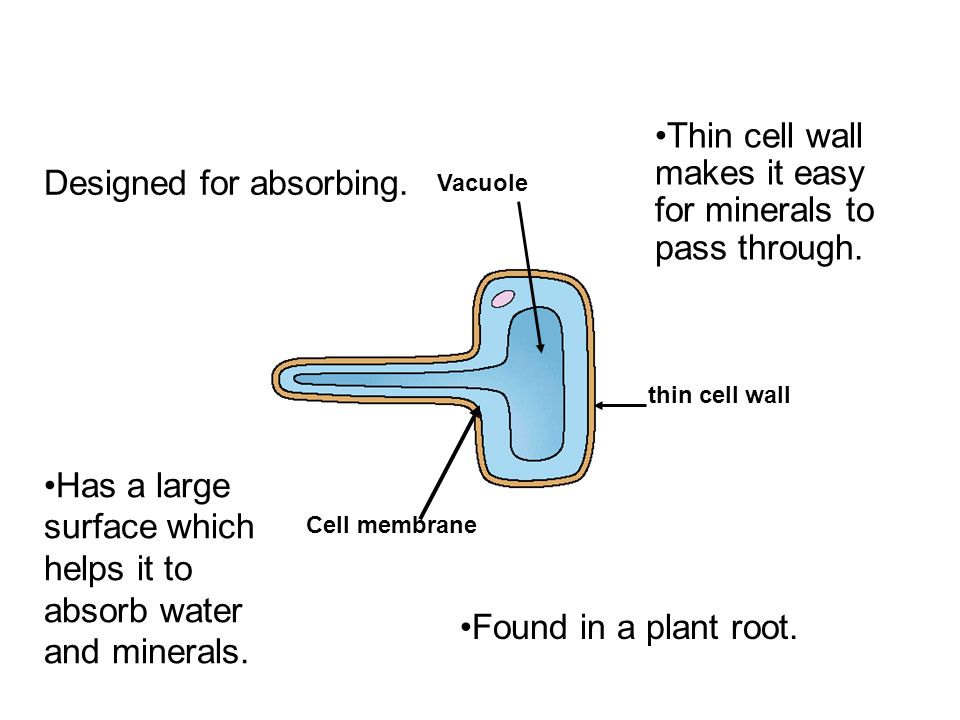
Root hairs are a very simple structure and can occur on the root tip in the thousands. They are basically an extension of the root s external cells. They are long and thin so they can penetrate between soil particles and they have a large surface area for absorption of water. As cells are lost among the soil particles new ones are added from the meristem behind the cap.
Oxygen from the air in soil particles diffuse into root hair and reach all the cells of the root where it is utilised in respiration. This region may be further subdivided into the zones of division and elongation according to the stage of growth of the cells. These represent water molecules. Behind this growing region is 3 the root hair or piliferous region.
The root hairs are where most water absorption happens. The function of root hairs is to collect water and mineral nutrients from the soil. They are lateral extensions of a single cell and invisible to the naked eye and light microscope. Root hairs are in contact with the air in the soil particles.
This ensures continued water supply to the plant. Use the hot glue to fix the root hair cell model to the right hand side of the brown foam core board. These cells constantly form at the top of the root of the plant so as others die new ones take their place. Carbon dioxide produced in the cells of the root during respiration goes out through the same root hair by the process of diffusion.
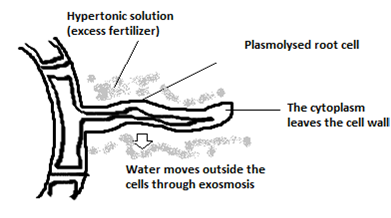
The root hair cells are delicate structures on the root of a plant which live only two to three weeks. Use the white glue to stick the typed explanation of the root hair cell and its function to the left hand side of the board. However new root hairs are formed in the older part of the zone of elongation so that the root hairs appear in the newer parts of the soil from where water has not yet been absorbed. This solution goes up through the roots to the rest of the plant.
A root hair of a vascular plant is a tubular outgrowth of a hair forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root. This allows the root hair coverage to remain the same despite root hairs constantly dying. Function of root hairs.