Root Hair Cell Not Labelled

The root hair cells are delicate structures on the root of a plant which live only two to three weeks.
Root hair cell not labelled. The growth of root hair cells. Facts about root hair cells. A root hair or absorbent hair the rhizoid of a vascular plant is a tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast a hair forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root as they are lateral extensions of a single cell and only rarely branched they are visible to the naked eye and light microscope. This allows the root hair coverage to remain the same despite root hairs constantly dying.
Facts about root hair cells 3. They are long and thin so they can penetrate between soil particles and they have a large surface area for absorption of water. Draw a labelled diagram of the root hair cell as it would appear if some fertilizer is added to the soil close to it. It also maintains the relationship of the plants with the microbes.
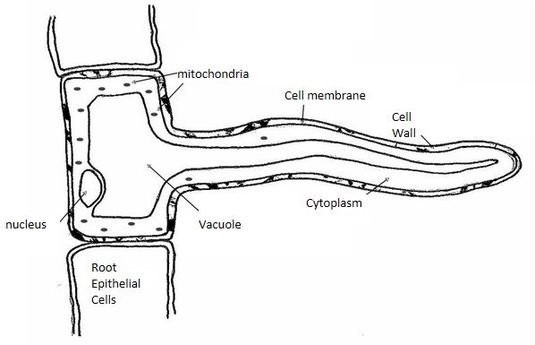
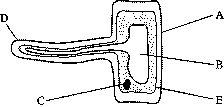
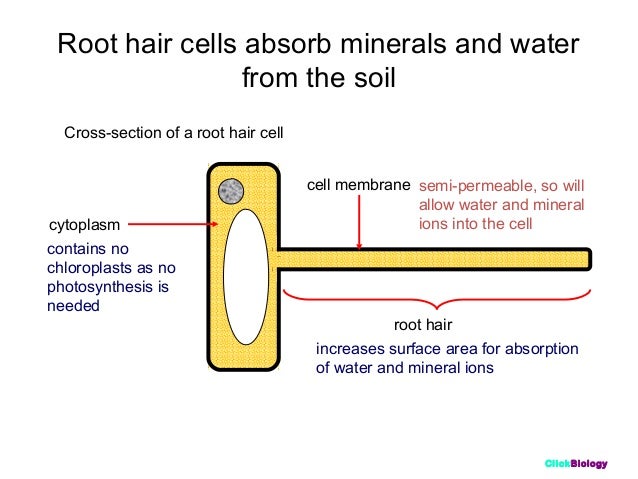
The function of the root hair cell is to obtain water from the ground and transport this to the xylem. This ensures continued water supply to the plant. This is a labelled diagram of a root hair cell. If you are interested to spot the root hair cell you have to notice the tip of the plant s root.
Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis. The root hair cell is not only important for absorbing the water. Root hair cells have thin cellwall large r sap vacoule presence of tonoplast long projections to increase surface area for water absorption all these structures are absent in liver cells. Home page 2d labelled diagram 3d diagram function of cell table of organelles sources of information 2d diagram of the root hair cell cytoplasm is a thick solution that fills each cell and is enclosed by the cell membrane.
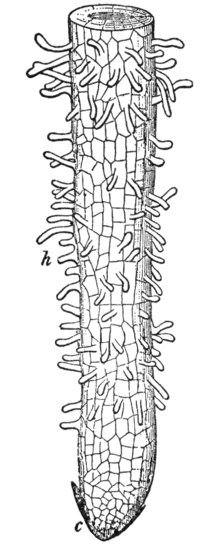
They are found only in the region of maturation of the root. However new root hairs are formed in the older part of the zone of elongation so that the root hairs appear in the newer parts of the soil from where water has not yet been absorbed. Root hair cells are adapted for this by having a large surface area to speed up osmosis.