Root Hair Cell Structure And Function
Cells lining the hair follicle are like shingles facing in the opposite direction.
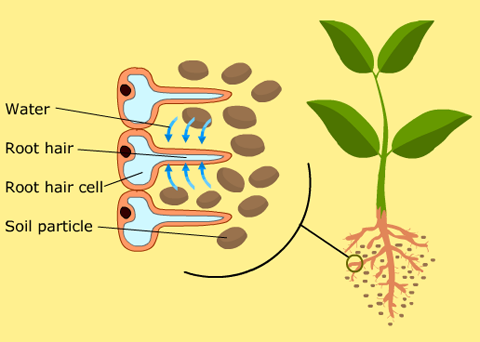
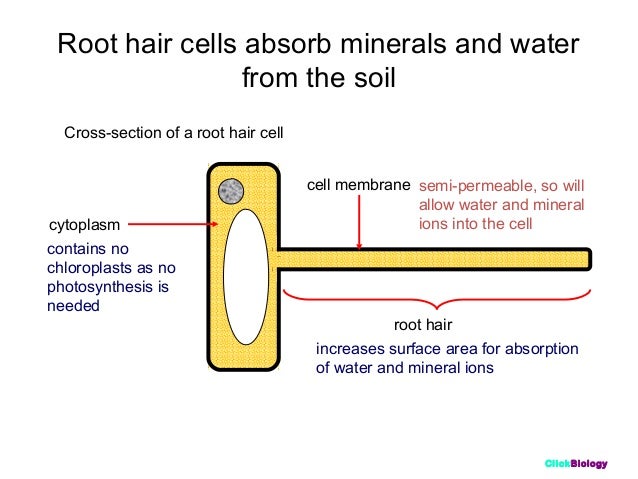
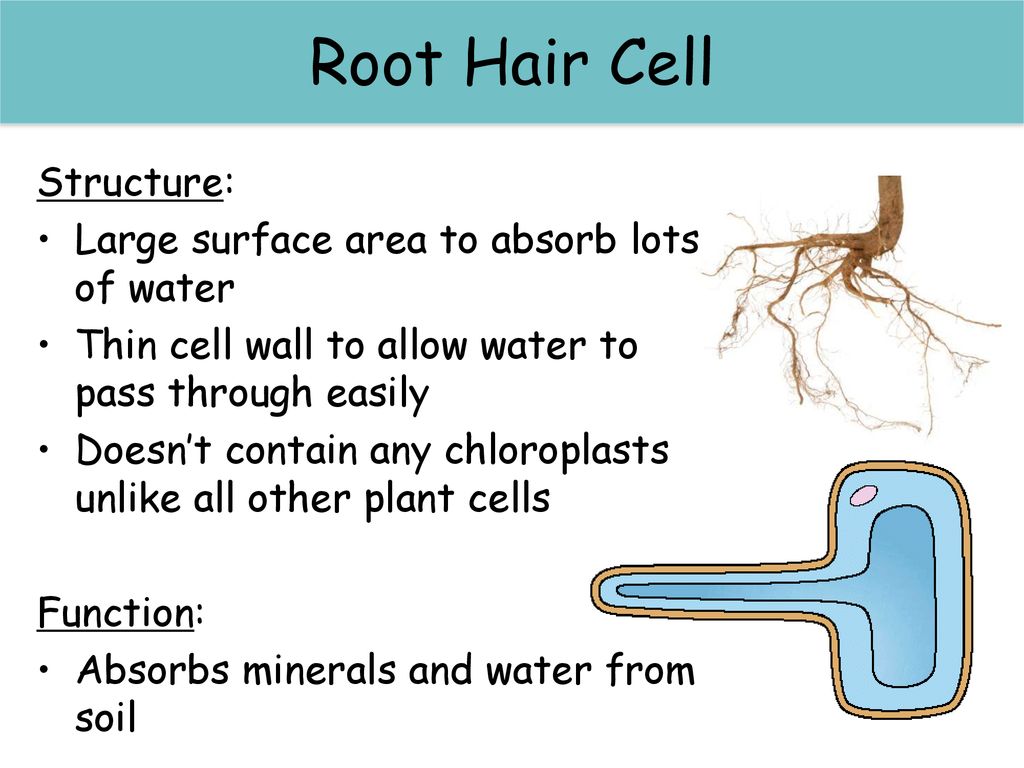
Root hair cell structure and function. The function of the root hair cell is to obtain water from the ground and transport this to the xylem. Root hair cells are adapted for this by having a large surface area to speed up osmosis. Increase the external surface area of the root for absorption of water and mineral ions the hair increases the surface area of the cell to make it more efficient in absorbing materials. This allows the root hair coverage to remain the same despite root hairs constantly dying.
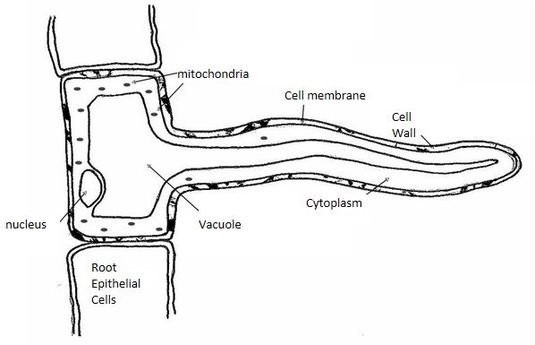
Another adaptation that they have is root hair cells have a large permanent vacuole. Root hairs are a very simple structure and can occur on the root tip in the thousands. The hair is an extension of the cell and not a separate cellular structure. Energy from the sun is eventually used to convert water into hydrogen and oxygen.
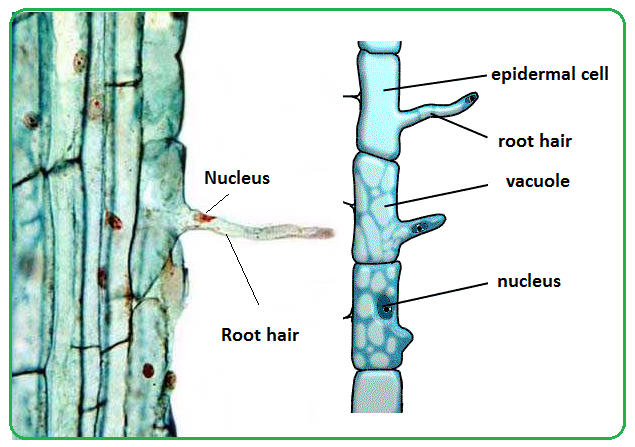
The structure of a root hair cell differs from other root cells in that it has a long thin extension supported by the central vacuole which greatly increases its surface area. Like other root cells it has a thick cell wall huge central vacuole and is separated from other root cells by a thin layer of cytoplasm. When a hair is pulled out this layer of follicle cells comes with it. The structure of the roots the water absorbed by the root hair cells passes through the plant in xylem tubes and eventually reaches the leaves.
The root hair cells are delicate structures on the root of a plant which live only two to three weeks. Function of root hairs. Functions of root hair cells. The hair follicle is a diagonal tube that contains the hair root.
They are found only in the region of maturation of the root. They interlock with the scales of the hair cuticle and resist pulling on the hair. They are basically an extension of the root s external cells.