Structure Of Root Hair Cell From A Plant
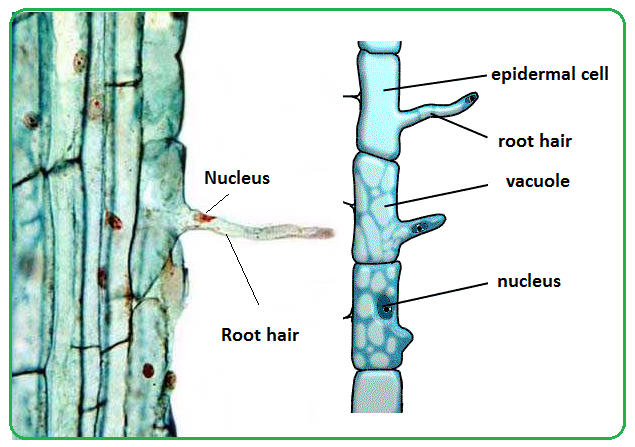
The nucleus of the epidermal cell is often found within the root hair.
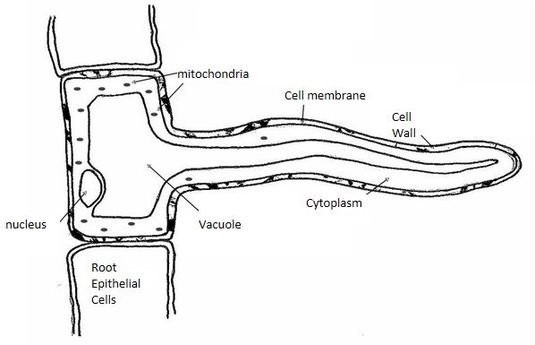
Structure of root hair cell from a plant. Root hair cells are specialised to perform a specific function. They also allow a plant to take in the minerals it needs to survive. Root hairs are extensions of the epidermal cells on the surface of the root and are continually being sloughed off by the soil and regrown. Structure of the root hairs diagram of the root hair structure.
Mutants from four phenotypic classes have been characterized in detail and genetic tests show that these result from single nuclear recessive mutations in four different genes designated rhd1 rhd2 rhd3 and rhd4. A root hair or absorbent hair the rhizoid of a vascular plant is a tubular outgrowth of a trichoblast a hair forming cell on the epidermis of a plant root as they are lateral extensions of a single cell and only rarely branched they are visible to the naked eye and light microscope. This allows the root hair coverage to remain the same despite root hairs constantly dying. In the study of the rye plant the roots were estimated to have some 14 billion root hairs.
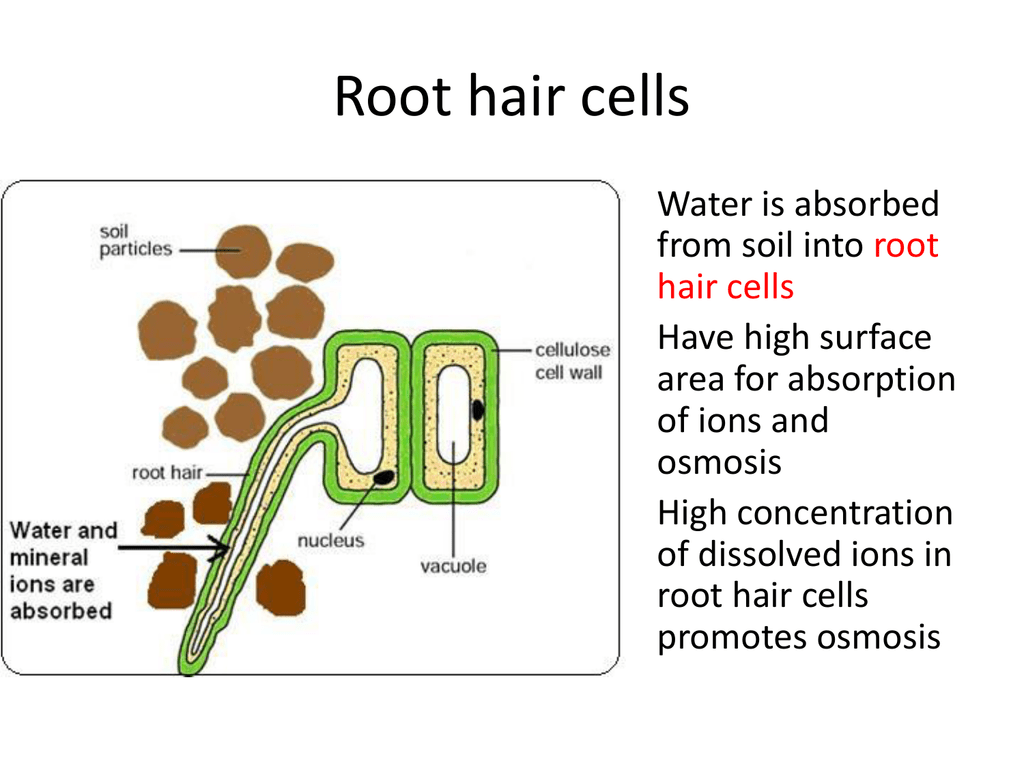
They are long and thin so they can penetrate between soil particles and they have a large surface area for absorption of water. These cells constantly form at the top of the root of the plant so as others die new ones take their place. Their structure allows the plant to absorb more water. Placed end to end they would have extended more than 10 000 kilometers.
The structure of a root hair cell differs from other root cells in that it has a long thin extension supported by the central vacuole which greatly increases its surface area. If a plant does not absorb enough water it will wilt or go floppy. The function of the root hair cell is to obtain water from the ground and transport this to the xylem. These cells are located underground.
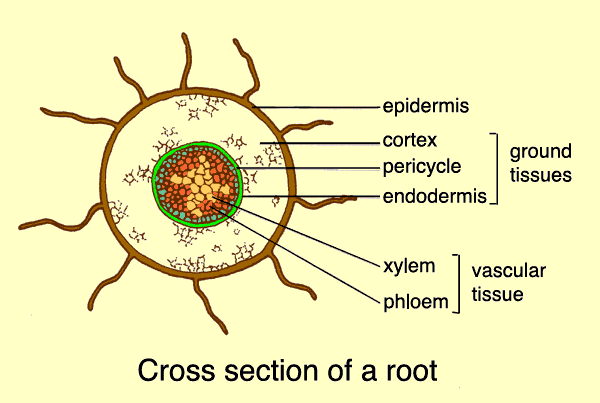
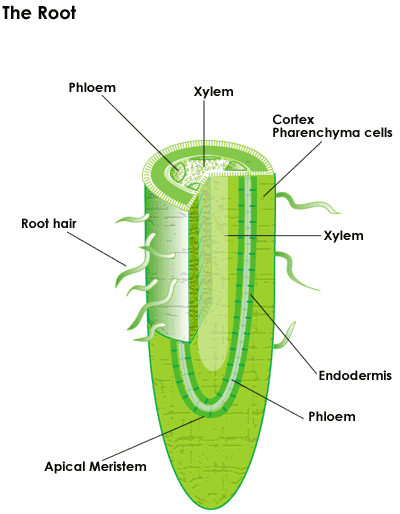
Root hairs are slender extensions of the epidermal cells themselves. Hydrogen is combined with the carbon dioxide to produce the food glucose for the plant whereas the oxygen which is a by product of the entire process is let out through the stomata. Like other root cells it has a thick cell wall huge central vacuole and is separated from other root cells by a thin layer of cytoplasm. They are found only in the region of maturation of the root.
The root hair cells are delicate structures on the root of a plant which live only two to three weeks. Root hair cells are adapted for this by having a large surface area to speed up osmosis. How is the root hair cell adapted to its function. Visual examination of roots from 12 000 mutagenized arabidopsis seedlings has led to the identification of more than 40 mutants impaired in root hair morphogenesis.
Plants absorb water from the soil by osmosis.